- January 15, 2022
- by:
- in: Blog
A ‘CT scan’ of the Universe across more than 5 billion light-years. (D. Schlegel/Berkeley Lab/DESI dataThe Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), currently pointed skyward from its home in the Nicholas U. Mayall Telescope at the Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, is tasked with tracking the expansion of space, to study dark energy and create the most detailed 3D map. of the Universe that was never assembled.It’s only been seven months since the DESI mission began, and we already have a record-breaking, stunning three-dimensional image of the galaxy all around us, demonstrating DESI’s capabilities and potential for mapping space. DESI has already cataloged and tracked over 7.5 million galaxies, with over a million new additions per month. When the scan is fully completed in 2026, more than 35 million galaxies would have been mapped, giving astronomers a huge library of data to mine. “There’s a lot of beauty in there,” says Lawrence astrophysicist Julien guy in California. “In the distribution of galaxies on the 3D map, there are huge clusters, filaments and voids.These are the largest structures in the Universe. But within them you will find an imprint of the early Universe and the story of its expansion since DESI is made up of 5,000 optical fibers, each individually controlled and positioned ionized by its own little robot These fibers must be precisely positioned within 10 microns, less than the thickness of a human hair, then catch glimpses of light as they filter through the Earth of the cosmos.Through this fiber network, the instrument takes color spectrum images of millions of galaxies, covering more than a third of the entire sky, before calculating how much the light has been redshifted – that is, how much it’s been pushed towards the red end of the spectrum due to the expansion of the Universe.As this light can take up to several billion years to reach Earth, it’s possible to use redshift data to see depth in the Universe: the greater the redshift, the farther away something is. What’s more, the structures mapped by DESI can be reverse engineered to see the initial formation that they started out in.The main objective of DESI is to reveal more about the dark energy that is thought to make up 70 percent of the Universe as well as speeding up its expansion. This dark energy could drive galaxies into an infinite expansion, cause them to collapse back on themselves or something in between – and cosmologists are keen to narrow down the options.[DESI] will help us search for clues about the nature of dark energy,” Carlos Frenk, a cosmologist at Durham University in the UK, told the BBC. We will also learn more about dark matter and the role it plays in how it happens, forms galaxies such as the Milky Way, and how the universe evolves.The 3D map that has already been released shows that scientists don’t have to wait for DESI to finish its work to start benefiting from its deep look into space explores whether or not small galaxies have their own black holes like large galaxies. The best way to spot a black hole is to identify the gas, dust and other material dragged into it, but that’s not easy to see in small galaxies – something where high-precision spectral data collected by DESI should help. Then there’s the study of quasars, particularly bright galaxies powered by supermassive black holes, which serve as clues to billions of years of space history. DESI will be used to test a hypothesis around quasars: that they start out surrounded by an envelope of dust that is chased away over time. The amount of dust around a quasar is believed to affect the color of the light it emits, making it a perfect job for DESI. The tool should be able to collect information on around 2.4 million quasars before its survey is complete.”DESI is really great because it collects much fainter, much redder objects,” says Durham University astronomer Victoria Fawcett. “We’re finding quite a few exotic systems, including large samples of rare objects that we’ve simply never seen able to study in detail before.Source: ScienceAlert
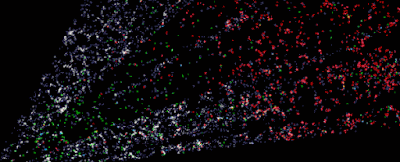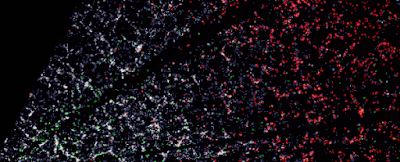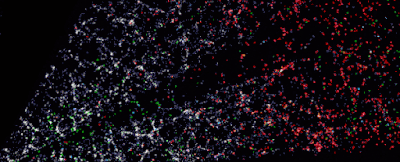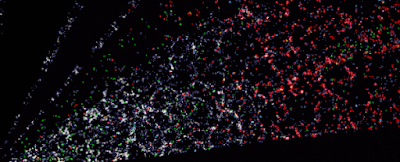 |
| A ‘CT scan’ of the Universe across more than 5 billion light-years. (D. Schlegel/Berkeley Lab/DESI data |
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), currently pointed skyward from its home in the Nicholas U. Mayall Telescope at the Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, is tasked with tracking the expansion of space, to study dark energy and create the most detailed 3D map. of the Universe that was never assembled.
It’s only been seven months since the DESI mission began, and we already have a record-breaking, stunning three-dimensional image of the galaxy all around us, demonstrating DESI’s capabilities and potential for mapping space.
DESI has already cataloged and tracked over 7.5 million galaxies, with over a million new additions per month. When the scan is fully completed in 2026, more than 35 million galaxies would have been mapped, giving astronomers a huge library of data to mine.
“There’s a lot of beauty in there,” says Lawrence astrophysicist Julien guy in California. “In the distribution of galaxies on the 3D map, there are huge clusters, filaments and voids.These are the largest structures in the Universe.
But within them you will find an imprint of the early Universe and the story of its expansion since DESI is made up of 5,000 optical fibers, each individually controlled and positioned ionized by its own little robot These fibers must be precisely positioned within 10 microns, less than the thickness of a human hair, then catch glimpses of light as they filter through the Earth of the cosmos.
Through this fiber network, the instrument takes color spectrum images of millions of galaxies, covering more than a third of the entire sky, before calculating how much the light has been redshifted – that is, how much it’s been pushed towards the red end of the spectrum due to the expansion of the Universe.
As this light can take up to several billion years to reach Earth, it’s possible to use redshift data to see depth in the Universe: the greater the redshift, the farther away something is. What’s more, the structures mapped by DESI can be reverse engineered to see the initial formation that they started out in.
The main objective of DESI is to reveal more about the dark energy that is thought to make up 70 percent of the Universe as well as speeding up its expansion. This dark energy could drive galaxies into an infinite expansion, cause them to collapse back on themselves or something in between – and cosmologists are keen to narrow down the options.
[DESI] will help us search for clues about the nature of dark energy,” Carlos Frenk, a cosmologist at Durham University in the UK, told the BBC. We will also learn more about dark matter and the role it plays in how it happens, forms galaxies such as the Milky Way, and how the universe evolves.
The 3D map that has already been released shows that scientists don’t have to wait for DESI to finish its work to start benefiting from its deep look into space explores whether or not small galaxies have their own black holes like large galaxies.
The best way to spot a black hole is to identify the gas, dust and other material dragged into it, but that’s not easy to see in small galaxies – something where high-precision spectral data collected by DESI should help. Then there’s the study of quasars
, particularly bright galaxies powered by supermassive black holes, which serve as clues to billions of years of space history.
DESI will be used to test a hypothesis around quasars: that they start out surrounded by an envelope of dust that is chased away over time. The amount of dust around a quasar is believed to affect the color of the light it emits, making it a perfect job for DESI.
The tool should be able to collect information on around 2.4 million quasars before its survey is complete.”DESI is really great because it collects much fainter, much redder objects,” says Durham University astronomer Victoria Fawcett.
“We’re finding quite a few exotic systems, including large samples of rare objects that we’ve simply never seen able to study in detail before.
Source: ScienceAlert