News: Luminate aims to make hair loss from chemotherapy a thing of the past
Hair loss resulting from chemotherapy is one of the most recognizable side effects in all of medicine, and for many is an unwanted public announcement of their condition and treatment. Luminate Medical may have a solution in a medical wearable that prevents the chemical cocktail from tainting hair follicles, preventing the worst of the loss
Hair loss resulting from chemotherapy is one of the most recognizable side effects in all of medicine, and for many is an unwanted public announcement of their condition and treatment. Luminate Medical may have a solution in a medical wearable that prevents the chemical cocktail from tainting hair follicles, preventing the worst of the loss and perhaps relegating this highly visible condition to the past.
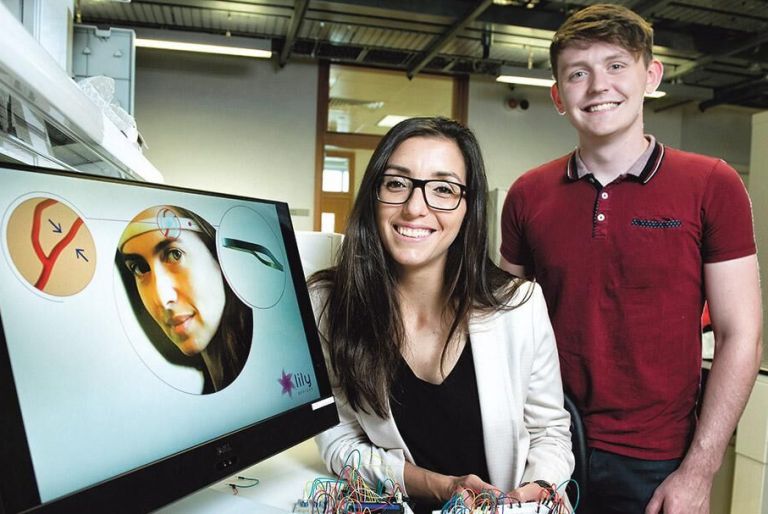
When Luminate CEO Aaron Hannon and his co-founder Bárbara Oliveira were asking patients and doctors about areas of cancer treatment that they could perhaps innovate in, “we were just astonished at how much hair loss dominated the conversation,” said Hannon. “So from then on out we’ve just been laser focused on making that something that doesn’t exist any more.”
When a patient is undergoing chemotherapy, the cancer-inhibiting drugs course through their entire body — anywhere the blood goes. This has a variety of side effects, like weakness and nausea, and on a longer time scale hair loss occurs as the substances affect the follicles. Luminate’s solution, developed in partnership with the National University of Ireland Galway, is to prevent the blood from reaching those cells in the first place.
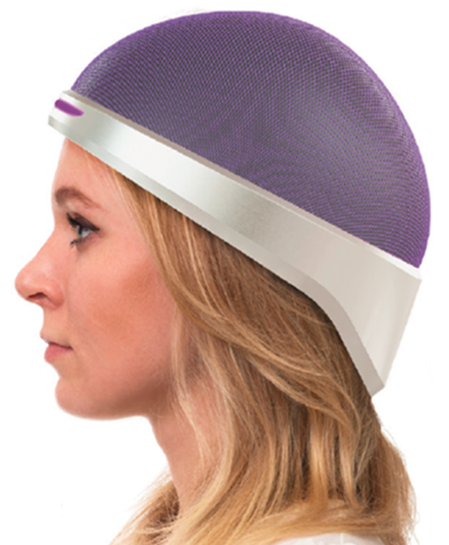
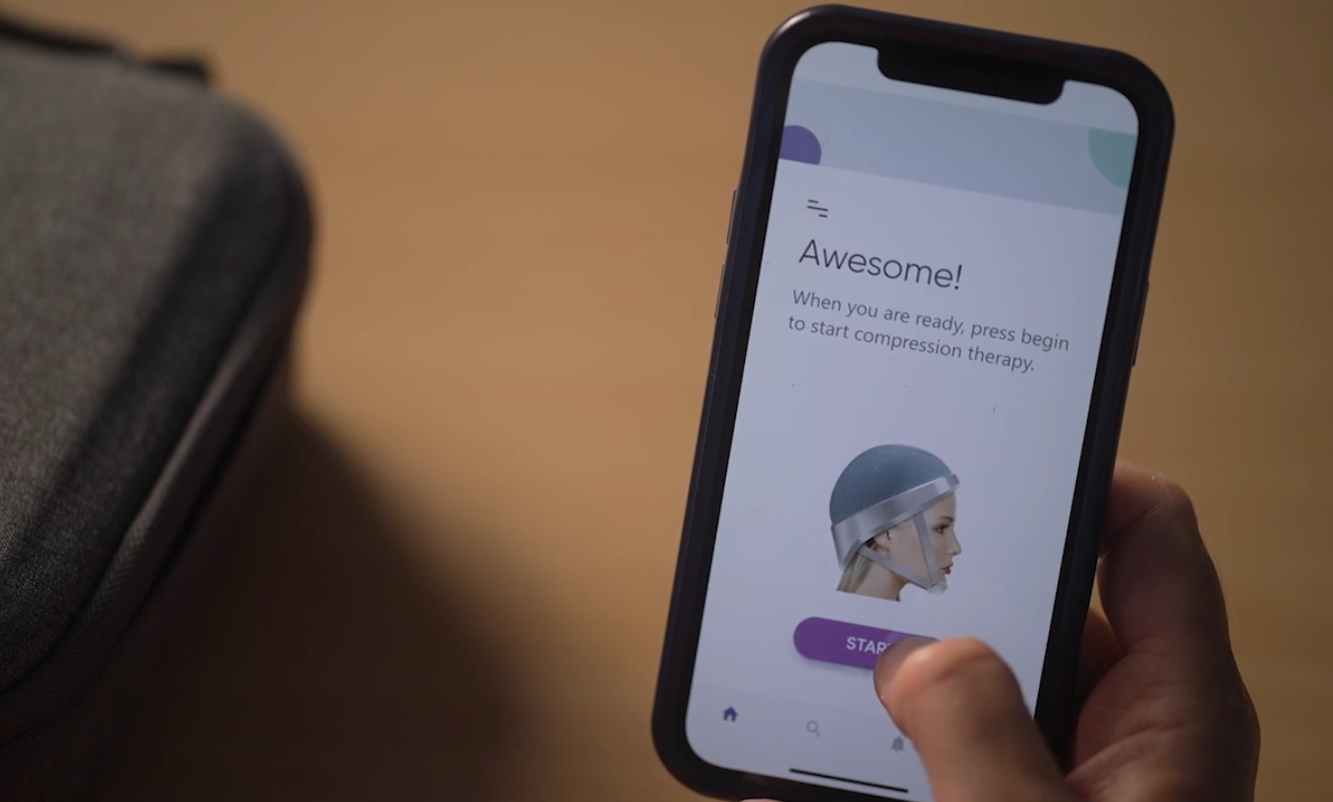
The device that effects this is a sort of mechanized compression garment for the head. If that sounds a bit sinister, don’t worry — the pressure comes from air bladders and pads pressing against the scalp, not screws or plates; Hannon says that it isn’t uncomfortable and pressure is carefully monitored.
There’s also no risk of damage from lack of blood flow in those cells. “Compression therapy has been really well studied,” he said. “There are years of literature around how long you can apply these therapies without damaging the cells. There’s a certain amount of mechanical engineering involved in making it both comfortable and effective.”
The patient wears the cap during and after the whole chemo session. By restricting blood flow to the skin of the scalp only, it allows the drugs to flow unimpeded to wherever the tumor or cancer site is while saving the hair follicles from damage.
Tests have been done on animals, which saw hair retention of around 80 percent with no adverse effects — and while full human trials are something that will need some time and approval to set up, initial tests of the headset’s bloodflow-blocking effects on healthy patients showed that it works exactly as expected on people as well.
“We’re really excited about the efficacy of this therapy because it works with lots of hair types,” said Hannon. That’s a real consideration, since a tech that only worked with short hair, straight hair, or some other subset of hairstyles would exclude far too many people.
As for competition, although there are some new treatments that cool the scalp instead of compressing it, Hannon noted that the most money is spent by far on wigs. An average of a thousand dollars per patient who opts for a wig means there’s considerable leeway for a device in that neighborhood.
Although hair loss is considered a medical condition by many insurance companies and other methods of reimbursement, and wigs are often covered, it will take time and lots of evidence to get Luminate’s device approved for those processes. But the team is confident that at around $1,500, the device is within the means of many as long as other costs are being picked up by insurance. People do, after all, spend that much and more not just on wigs but on other hair retention products and methods. If there was a checkbox for “don’t lose hair” on the chemo forms with a $1,500 price tag, a whole lot of people would check it without a second thought.
Ultimately, however, Luminate wants to be able to offer the device also to those who can’t afford the cost out of pocket, so they are progressing towards FDA approval and a U.S. launch, with Europe and others to come.
So far Luminate, just graduating from Y Combinator’s Summer 2021 batch, has been lucky enough to operate on funds provided through grants from the Irish government, which are of course non-dilutive. While more capital will almost certainly be required come time for scaling and international launch, right now the team is focused on getting the device into the hands (and onto the heads) of its first set of patients.