- September 15, 2021
- by:
- in: Blog
So what exactly is “signal” in growth marketing? It can carry many different meanings, but holistically speaking, it’s the event data in our arsenal to help guide decisions.
Jonathan Martinez
Contributor
Jonathan Martinez is a former YouTuber, UC Berkeley alum and growth marketing nerd who’s helped scale Uber, Postmates, Chime and various startups.
More posts by this contributor
Unlike a weak phone signal solely causing a grainy sound, in growth marketing, it can mean the difference between a successful program or a massive cash bleed. As we move toward an increasingly privacy-centric world, it is even more necessary for companies to nail down signal early on.
So what exactly is “signal” in growth marketing? It can carry many different meanings, but holistically speaking, it’s the event data in our arsenal to help guide decisions. When it comes to paid acquisition, it’s vital to optimize and pass back the correct event data to paid channels. This is so that targeting and bidding algorithms have the most enriched data to utilize.
I’ve seen startups spend thousands of dollars inefficiently as a result of not having optimal signal in their paid acquisition campaigns. I’ve also spent millions at companies such as Postmates refining our signal to the best possible state. I’d like every startup to avoid the painful mistake of not having this set up correctly, instead making the most of every important ad dollar.
The selection
When starting out, it may seem obvious to optimize toward a north-star metric such as a purchase. If spend is very minimal, that could mean that the conversion volume will be low across campaigns. On the flip side, if the optimization event is set at a top-of-funnel event such as a landing page view, the signal strength may be very weak. The reason that the strength may be weak is due to passing back a low-intent event as successful to the paid channels. By marking a landing page view as successful, paid channels such as Facebook will continue to find users that are similar to these lower-propensity users that are converting.
Let’s take an example of a health-and-wellness app with a goal of driving memberships to their coaching program. They’re just starting out with exploring paid acquisition and spending $5,000 per week on Facebook. Below is a look at their events in the funnel, weekly volume and cost per event:
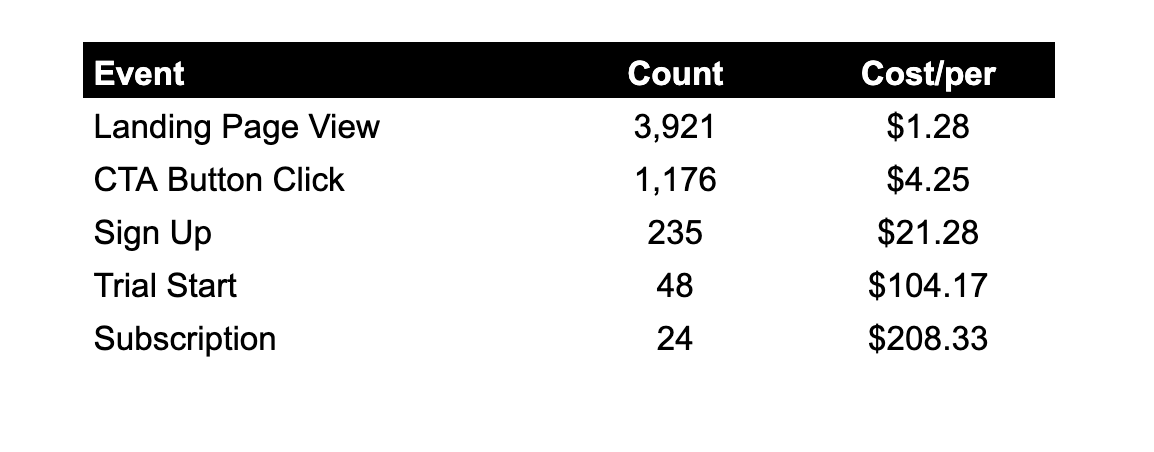
Example of a health-and-wellness app and their weekly conversion volume at $5,000 spend. Image Credits: Jonathan Martinez
In the above example, we can see that there’s significant volume for landing page views. As we go down the simplified flow, there is less volume as users drop off the funnel. Almost everyone’s instinct would be to optimize for either the landing page view, because there’s so much data, or the subscription event, because it’s the strongest. I would argue (after extensive testing across multiple ad accounts) that neither of these events would be the correct pick. With landing page views as an optimization event, the users have an egregiously low propensity since the landing page view to subscription conversion rate is 0.61%.
The correct event to optimize for here would either be sign up or trial start because they have sufficient enough volume and are strong signals of a user converting to the north-star metric (subscription). Looking at the conversion rate between sign up and subscription, it’s a much healthier 10.21%, versus the 0.61% from landing page view.
I’m always a huge proponent of testing all events, as there can definitely be big surprises in what may work best for you. When testing events, make sure that there’s a stat-sig baseline that’s being followed to make decisions. Additionally, I think it’s a great practice to test events regularly early on because conversion rates can change as other channel variables are adjusted.
Flow adjustments
In certain cases, the current events that are set up aren’t optimal for paid acquisition campaigns. I’ve seen this happen frequently with startups that have long windows of time between conversion events. Take a startup such as Thumbtack, which provides a marketplace of providers who can help with home repairs. After someone signs up to their app, the user may place a request but not hire someone until a few weeks later. In this case, making flow adjustments could potentially improve the signal and data that you collect from users.
A solution that Thumbtack could implement to gather a stronger signal would be to add another step between the request being placed and hiring someone. This could potentially be a survey with propensity check questions that could ask how soon the user needs help or how important their project is from a 1–10.
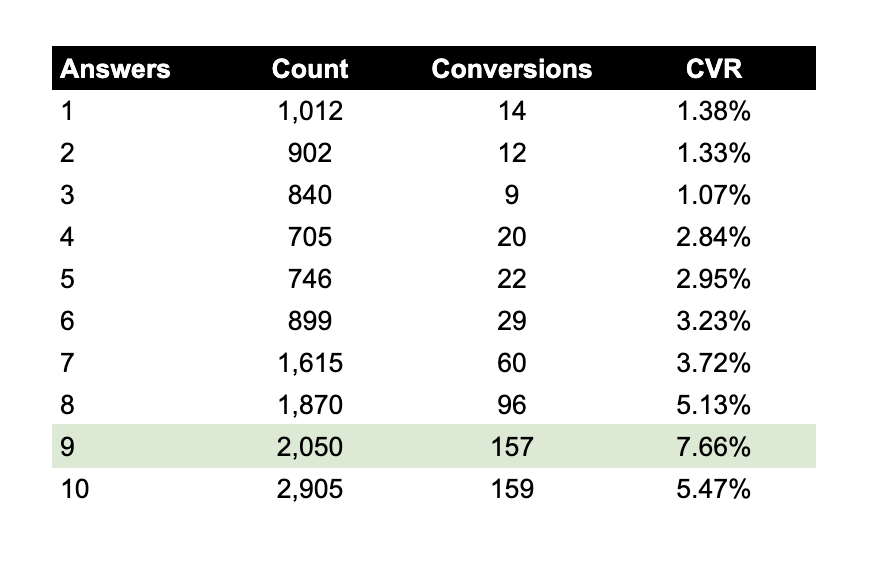
Example of in-app survey responses to “How important is your project?” Image Credits: Jonathan Martinez.
After accumulating the data, if there’s a high correlation between survey answers and someone starting their project, we can start to explore optimizing for that event.
In the above example, we see that users who responded with “9” have a 7.66% likelihood to convert. Therefore, this should be the event we optimize for. Artificially adding steps that qualify users in a longer flow can help steer optimization targeting in the right direction.
Enhancing signal
Let’s imagine that you have the most ideal flow that captures large volumes of event signal without much of a delay to your optimization event. That’s still far from perfect. There are myriad solutions that can be implemented to further enhance the signal.
For Facebook specifically, there are connections such as CAPI that can be integrated to pass back data in a more accurate way. CAPI is a method of passing back web events server-to-server rather than relying on cookies and the Facebook pixel. This helps mitigate browsers that block cookies or users who may delete their web history. This is just one example. I won’t run through all the channels, but each has its own solution to help enhance event signal being passed back to it.
iOS 14 signal
This wouldn’t be a column written in 2021 without mention of iOS 14 and the strategies that can be leveraged for this growing user segment. I’ve written another piece about iOS-14-specific tactics, but I’ll cover it here on a broad level. If the north-star metric (i.e., purchase) event can be triggered within 24 hours of the initial app launch, then that’s golden.
This would bring large volumes of high-intent data that would not be at the mercy of the SKAD 24-hour event timer. For most companies, this may sound like a lofty goal, so the target should be to have an event fire within 24 hours that is a high-likelihood indicator of someone completing your north-star metric. Think of which events happen in the flow that lead to someone eventually purchasing. Maybe someone adding a payment method happens within 24 hours and historically has a 90% conversion rate to someone purchasing. An “add payment info” event would be a great conversion event to use in this case. The landscape of iOS 14 is constantly changing but this should apply for the immediate future.
Incrementality and staying ahead
As a rule of thumb, incrementality checks should constantly be performed in growth marketing. It gives an important read on whether advertising dollars are bringing in users that wouldn’t have converted had they not seen an ad.
When comparing optimization events, this rule still applies. Make sure that costs per action aren’t the only metric that’s being used as a measure of success, but instead, use the incremental lift on each conversion event as the ultimate key performance indicator. In this piece, I detail how to run lean incrementality tests without swarms of data scientists.
So how do you stay ahead and continue moving the needle on your growth marketing campaigns? First and foremost, constantly question the events you’re optimizing for. And second, leave no stone unturned.
If you’re using the same optimization event forever, it will be a disservice to your campaign performance potential. By experimenting with flow changes and running tests on new events, you’ll be way ahead of the curve. When iterating on the flow, think about user behavior and events from the user’s perspective. Which flow events, if added, would correlate to a high propensity conversion segment?